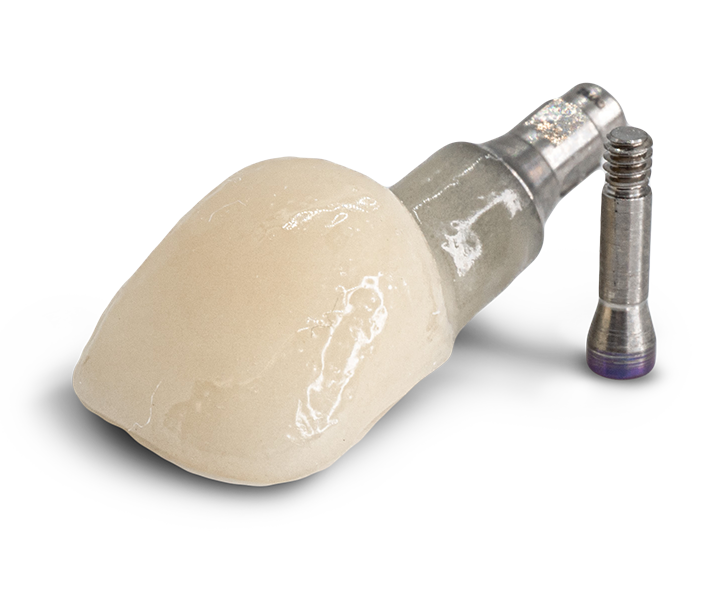
Cementable Implant Crowns
A cementable implant crown is designed to be luted onto an abutment using dental cement.
Screw-Retained Implant Crowns
Screw-retained crowns attach directly to the implant or abutment with a fixation screw, leaving a small access channel that is later filled.
Screwmentable Implant Crowns
Screwmentable crowns combine the advantages of both cementable and screw-retained designs. The crown is cemented extraorally onto a screw-retained abutment, then delivered and secured as a single unit.